Curriculum Guides | Stage 1 Curriculum Guide
Stage 1 Curriculum Guide
For Year 10 students entering Year 11 (SACE Stage 1)
Table of contents
- Senior Years Curriculum
- Process for Subject Selection
- SACE Overview
- Introduction to the SACE
- Flexible Industry Pathways and Vocational Education and Training
- English (Global Perspectives) Pathways
- HASS (Global Perspectives) Pathways
- Language (Global Perspectives) Pathways
- Lifestyle Choices Pathways
- The Arts Pathways
- Technologies (STEM) Pathways
- Maths (STEM) Pathways
- Science (STEM) Pathways
- Futures Ready
- Further Information
Senior Years Curriculum
This guide describes the learning offered for Year 11 students at Adelaide Botanic High School in 2024 as they move into SACE Stage 1 (South Australian Certificate of Education) and beyond.
They will be supported to become familiar with the range of SACE learning options, learn the terminology used to describe senior school curriculum and understand the requirements of the SACE and VET (Vocational Education Training).
We expect students to explore learning choices that give them every opportunity to achieve success for their dreams and goals.
Alistair Brown
Principal

Process for Subject Selection
Term 3 Subject Selection Milestones
| WEEK 4 | 2024 Curriculum Guide is released online |
| Studio One and Connect: Subject selection focus and preparing for Learning Pathway Conversations | |
| Student Pathway Expo - Adelaide Convention Centre Wednesday, 16 August. Year 10's attend in Connect groups in 2 hours blocks through the day | |
| WEEK 5 | Studio One: Subject selection focus and preparing for Learning Pathway Conversations |
| Spotlight Session: Year 10 transition into Year 11 SACE | |
| WEEK 6 | Online subject selection opens in Web Preferences |
| Studio One: Subject selection focus and preparing for Learning Pathway Conversations | |
| WEEK 7 | Thursday, 7 September Learning Pathway Conversations - face to face during the day |
SACE Overview
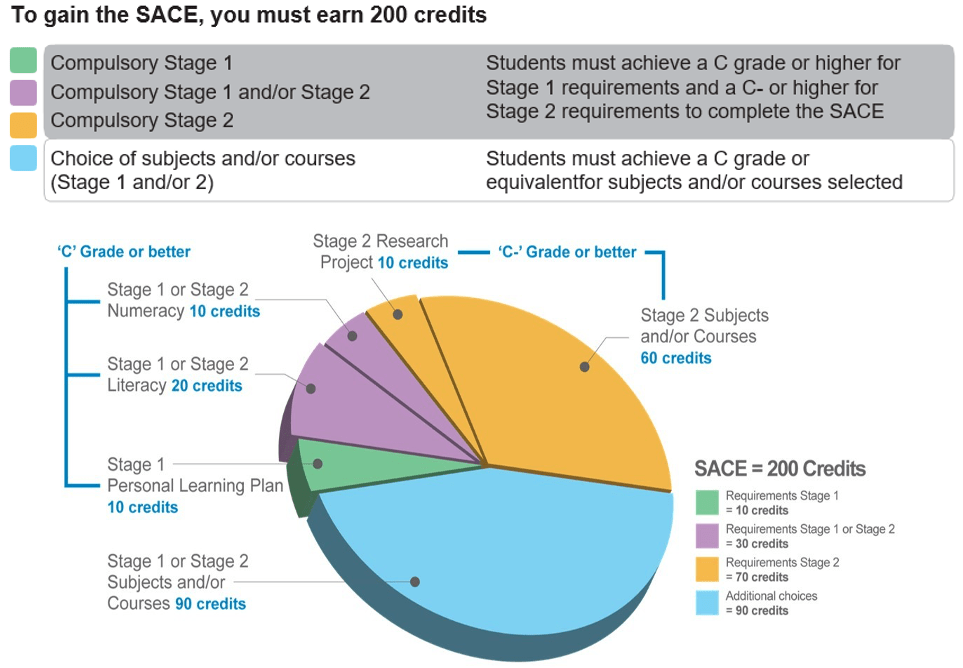
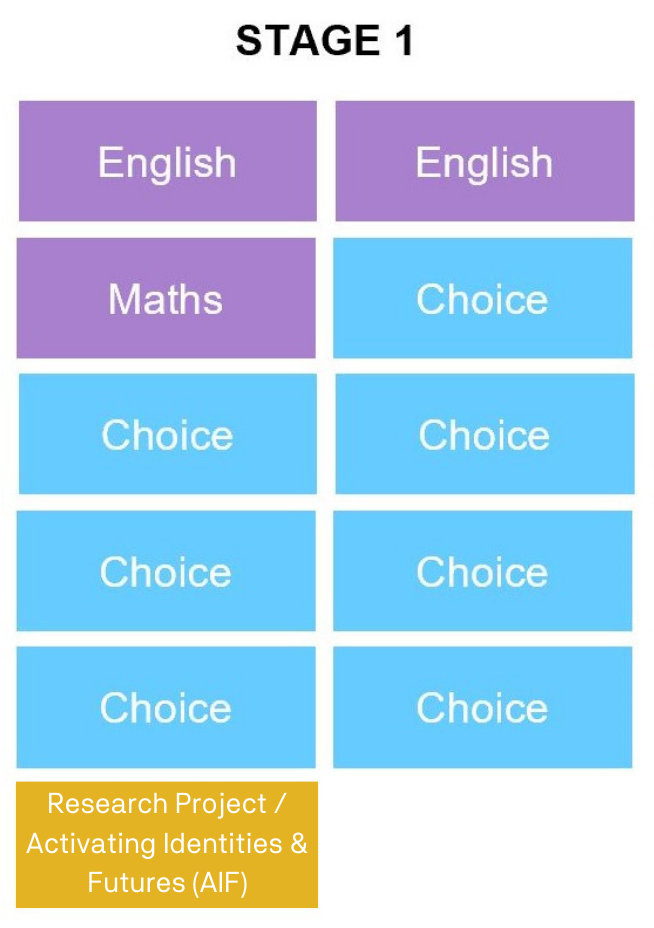
The Research Project/AIF form part of the Stage 1 Learning Program.
Introduction to the SACE
The SACE is a modern, internationally-recognised secondary school qualification designed to equip students with the skills, knowledge, and personal capabilities to successfully participate in our fast-paced global society.
Students will be awarded the SACE when they successfully complete requirements that include a range of skills and subjects they may study at school or may have acquired through other education, training or experience.
The SACE has been updated and strengthened to ensure it meets the needs of today’s young people. The SACE will help students develop the skills and knowledge they need to succeed – whether they are headed for further education and training, university, an apprenticeship or straight into the workforce.
As part of the SACE students will be expected to gain and demonstrate essential skills and knowledge for their future, focusing on communication, citizenship, personal development, work and learning. These are called ‘capabilities’, and are a combination of the skills, knowledge, and attributes students will need to be responsible and active members of the community.
SACE requirements
At ABHS, students start their SACE journey with Exploring Identities and Futures (EIF) in Year 10, their selection of Stage 1 subjects in Year 11 including the compulsory Maths and English choices, Research Project/Activating Identities and Futures (AIF), and their selection of Stage 2 subjects in Year 12 (including recognised courses).
Modified SACE
Students with learning difficulties or disability, that result in significant impairment in intellectual functioning and/or adaptive behaviours, and who are unable to meet Stage 1 or 2 subject learning requirements in one or more mainstream SACE subjects, may negotiate to undertake Modified SACE subjects.
Students will select subjects from the subject offerings at Adelaide Botanic High School and negotiate individual learning goals aligned with their One Plan Goals, which accommodate their learning needs and interests, and which allow them to develop knowledge and skills connected to their aspirations and pathways beyond school.
Adelaide Botanic High School Inclusion and SACE Leaders will work with families considering a Modified SACE Pathway to ensure eligibility requirements are met.
Subjects undertaken as a Modified version as part of SACE completion precludes an ATAR being gained.
SACE special provisions
Special provisions are available if a student has a disability, illness, experiences misadventure, or an unforeseen circumstance which significantly impacts their ability to participate in an assessment.
If a student applies for special provisions they need to provide evidence of how this impacts their ability to access assessment conditions. After checking for special provisions eligibility, students can apply through ABHS. In consultation with the student and based on evidence provided, the school will determine what type of reasonable adjustments are appropriate. On approval, reasonable adjustments are made.
Further information is available at SACE special provisions.
Further information
Further information is available on the SACE website, which is designed to support students and families.
Students are encouraged to talk with their teachers and the Leadership team about their study options.
Flexible Industry Pathways and Vocational Education and Training
Vocational education and training (VET) courses are opportunities for students in Years 11 and 12 to access a range of competencies and flexible industry pathways (FIPs) to develop industry endorsed skills and gain a head start on their career while completing their SACE. FIPs are undertaken either as standalone VET courses or in combination with employment via a training contract.
FIPs are aimed to support young people engage with entry level skilled careers in identified industry areas. Information on these industries and potential career pathways can be found on the Student Pathways website.
There are many options available through various nominated training organisations (NTOs). Adelaide Botanic High School is a member of the East Adelaide Secondary Vocational Alliance (EASVA), comprising of secondary schools working to make VET accessible to students. Where students have a genuine interest in a course not offered through EASVA, they should discuss this with the Futures Ready Student Pathways Senior Leader at ABHS to investigate viability of study during or post school.
Non FIP courses such as Cert III Business, Cert III Fitness etc being undertaken for ATAR purposes only outside of a traineeship, are not supported by ABHS or Department for Education Schools. No timetabling, enrolment or payment support can be provided. The school can support with SACE resulting if requested otherwise results should be provided direct to the SACE Board by the student.
VET Course Delivery
VET courses are run at numerous venues depending on the course. Within EASVA, host schools run courses in partnership with NTOs on their site, others may be directly at the NTOs campus or online.
Examples of school hosted courses include Certificate II in Automotive Servicing hosted at Charles Campbell College run by Quality Automotive Training or the Certificate II in Electrotechnology (Career Start) hosted at Marden Senior College with PEER or our own ABHS-hosted hospitality courses.
VET courses hosted at ABHS
ABHS Hosts Certificate II in Hospitality and Certificate II in Cookery in partnership with the Adelaide Institute of Hospitality.
These courses are delivered by professional industry trainers utilising the school’s contemporary, well-equipped commercial kitchen and training restaurant.
How do students enrol in a VET course?
It is important that any student wishing to enrol in a VET course conducts thorough research to ensure a genuine interest in the field and its suitability to their career pathway and SACE pattern.
Students will be asked complete an expression of interest form to begin the application process for EASVA courses or directly via the school for other NTOs.
All students applying for courses undertake a VET Readiness Orientation (VETRO) with the training provider (NTO) as part of the selection process prior to being offered any place. This will generally cover prior experience and motivation as well as literacy and numeracy benchmarking. In many cases, students will benefit from completing a work placement to inform their decision.
Meeting with the Futures Ready Student Pathways Senior Leader will provide an opportunity to clarify information and assist with the enrolment process.
Further information
For further information about VET in the SACE visit the SACE website.
